Common Conditions
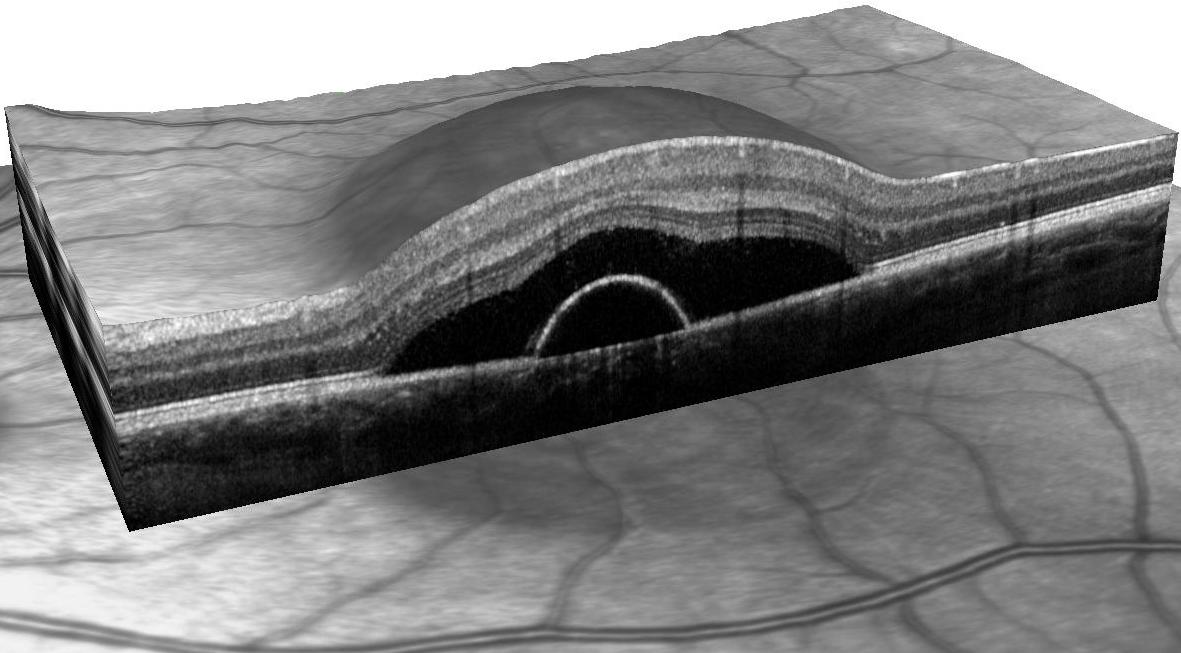
There is a revolutionary diagnostic technique that allows the ophthalmologist to see a detailed cross section of the layers of the retina and vitreous body. Disease is detected while the conventional view of the retina is still normal. Early glaucoma is revealed by a thinning of the nerve fiber layer, diabetic retinopathy by cystic thickening of the retina. Macular degeneration causes deformation to the deep layers of the retina. Abnormal membranes at the interface of the retina and vitreous are revealed before they distort vision.
Deposits in the vitreous humor creating floaters
These are usually caused by the collapse of the vitreous body in mid life which is entirely normal. Rarely, it can tear the retina resulting in a vision threatening retinal detachment. When discovered before the retina detaches, these tears are easily sealed with laser light.
Very common, especially in women; artificial tears usually suffice. Causing the body's own tears to remain longer on the eye is also effective and convenient. Dissolvable plugs are placed in a small lower lid opening that normally drains away tears. This takes only a few seconds. If the symptoms of dryness, grittiness and irritation are improved, a non-dissolvable plug is placed later.
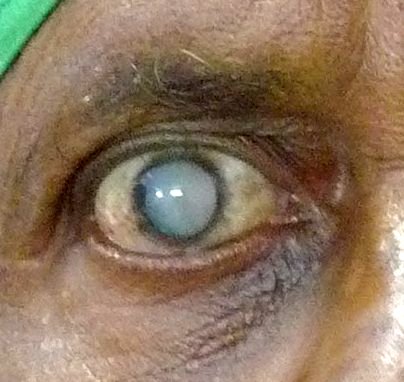
A mature cataract
A frequent cause of glare, especially when driving at night. Modern cataract surgery is much less intrusive than in the past. Before deciding on surgery the need for glasses must be evaluated as well as the presence of macular degeneration. A significant cataract will usually cause vision to drop markedly when a glare tester is used in the office. Vision will improve when tested with a pinhole, indicating that behind the cataract lies a healthy retina and a good surgical result can be expected.
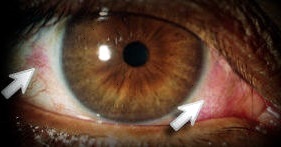
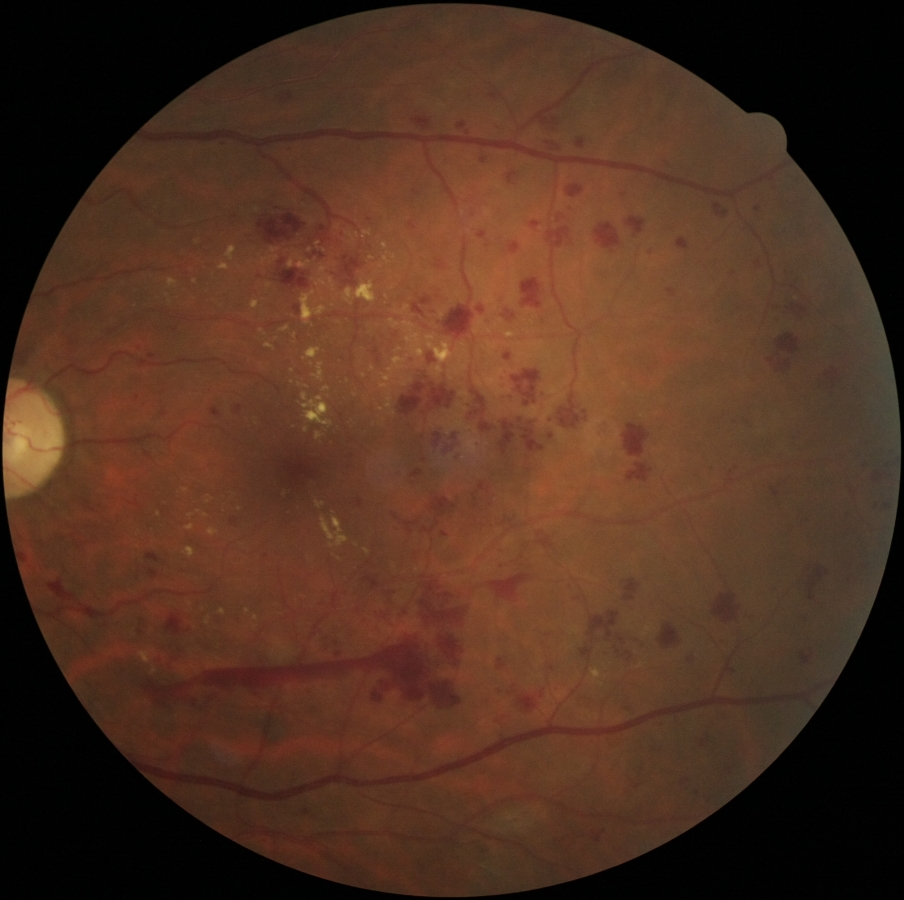
Photo of an eye with Diabetic Retinopathy
Public health doctors recommend that the retina of every diabetic be examined once a year and any significant bleeding that occurs be considered for laser treatment. Spectral domain OCT shows all the retinal layers in both cross section and in three dimensions enabling us to see previously invisible processes like subtle swelling of the retina. This technique is useful in macular degeneration, and glaucoma as well.
Tunneling effect caused by glaucoma
Progressive damage to the optic nerve with loss of peripheral vision is the hallmark of this disease. Elevated eye pressure is often present but not always. Treatment involves lowering eye pressure with one or more of four classes of eye drops, using light from a tiny laser beam to repair the obstructed drains within the eye or, rarely, bypassing the obstructed drainage system surgically. Fortunately we have several optical methods to measure optic nerve damage and establish progression. Side vision is tested with white light, colored light or motion. Pressure is measured after an anesthetic drop. No air puff is used.
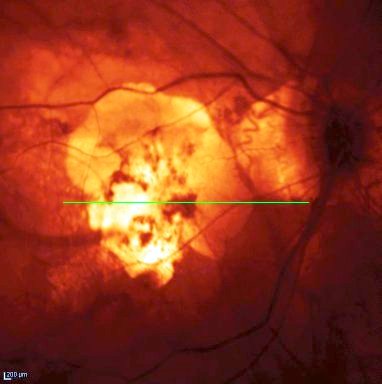
Photo of an eye with macular degeneration
More and more common as people age. Macular degeneration comes in two forms. Dry macular degeneration is a slow process which damages the retinal cells that give us sharp vision, especially for reading. Wet macular degeneration usually occurs suddenly with bleeding into a macula already afflicted with dry macular degeneration. Prevention involves vitamin therapy for dry macular degeneration. Wet macular degeneration requires use of medications that close off the vessels that are bleeding into the macula. Diagnosis is made by visualizing the macula by Spectral Domain OCT, which allows visualization of all retinal layers in cross section.
A fine local resource for those who have poor vision even after the best glasses and medical treatment is the Low Vision Service at UC Berkeley. Patients with Macular Degeneration or any condition which cannot be corrected to their satisfaction should arrange for a low vision evaluation. Generally, devices are dispensed which enlarge images so that they fall on the part of the retina that still sees well. A simple example is a proper magnifier and good illumination. A more elaborate example is a video reading machine in which a book is laid under a camera and read on a TV screen. The art is in diminishing unwanted distortions and making sure the image is at the correct distance. The examination costs $274 and the devices are extra. This service is sometimes covered by insurance. There is a detailed form that is completed by the ophthalmologist who will make the referral.